- Kidney Stone Treatment
- Andrology consultation
- Urology consultation
- Urinary tract infections
- Pediatric Urologist
- Cancer Surgery
- Urethral Stricture treatment
- CAPD cathersiation
- AV Fistula Surgery
- Male Infertility & Andrology
- Reconstructive Urology
- Genitourinary tract Cancer
- Prostate Cancer Treatment
- Bladder Cancer
- Kidney Cancer
- Ureter stones
- Bladder Stones
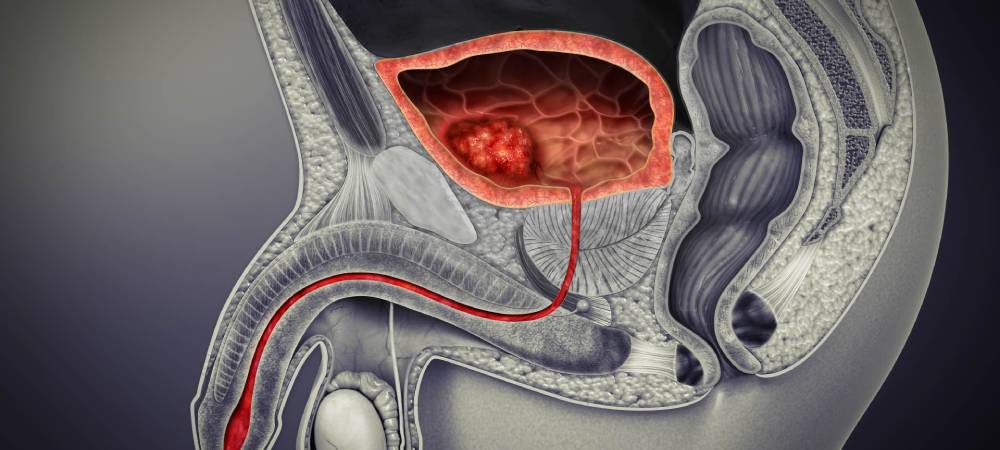
What is Bladder Cancer?
Bladder cancer is the most common type of cancer that begins in the cells of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow muscular organ in your lower abdomen that stores urine.
Bladder cancer most often begins in the cells (urothelial cells) that line the inside of your bladder. Urothelial cells are also found in your kidneys and the tubes (ureters) that connect the kidneys to the bladder. Urothelial cancer can happen in the kidneys and ureters, too, but it’s much more common in the bladder.
Most bladder cancers are diagnosed at an early stage when the cancer is highly treatable.
What are the symptoms of Bladder Cancer?
Bladder cancer signs and symptoms may include:
- Blood in the urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola-colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test
- Frequent urination
- Painful urination
- Back pain
What are the Risk Factors?
Factors that may increase bladder cancer risk include:
- Smoking: Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes may increase the risk of bladder cancer by causing harmful chemicals to accumulate in the urine.
- Increasing age: Bladder cancer risk increases as you age. Though it can occur at any age.
- Being male: Men are more likely to develop bladder cancer than women are.
- Previous cancer treatment: Treatment with the anti-cancer drug cyclophosphamide increases the risk of bladder cancer.
- Family history of cancer: If you’ve had or one of your relatives had bladder cancer, you’re more likely to get it again.
How is bladder cancer diagnosed?
Your doctor may diagnose bladder cancer using one or more of the following methods:
- a urinalysis
- an internal examination, which involves your doctor inserting gloved fingers into your vagina or rectum to feel for lumps that may indicate a cancerous growth
- a cystoscopy, which involves your doctor inserting a narrow tube that has a small camera on it through your urethra to see inside your bladder
- a biopsy in which your doctor inserts a small tool through your urethra and takes a small sample of tissue from your bladder to test for cancer
- a CT scan to view the bladder
- an intravenous pyelogram (IVP)
- X-rays
How to Book An Appointment?
Dr. Yogesh Torkadi at Urovision Kidney Super Speciality Clinic provides the best treatment for various urological diseases in Sangamner. For more information about our comprehensive treatment options, or to request an appointment with the best Urosurgeon in Sangamner call 07666109771 or Click on Book Appointment for online booking with your near hospital.

